3D cell culture:overview and news
|
On this page, we give a brief overview over the basics of 3D cell culture with cell lines and primary cells. We describe differences between the classic 2D- / monolayer culture and 3D models. We give examples for 3D models, co-culture systems, matrices and fields of application in research, pharmaceutical labs and medicine. The following topics are covered below: |
|
3D cell culture basics
How do 2D and 3D cell culture differ?
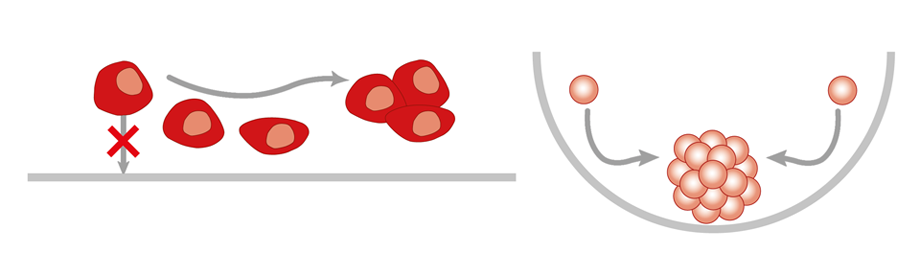
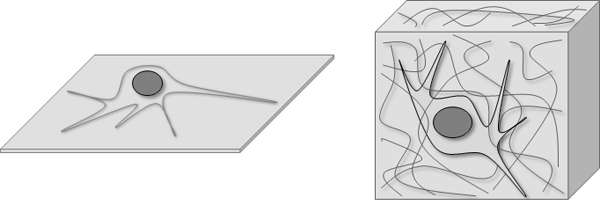
The normal standard type of cell culture is 2D- or monolayer culture of adherent cells in cell culture vessels like dishes, plates, multiwell plates, flasks etc. Hierdurch haben die Zellen in Kultur nur ein Oberfläche mit der sie Kontakt haben und die Nachbarzellen sind nur in 2 Ebenen (2D) neben den Zellen engeordnet. Diese Form nennt man auch Monolayer-Wachstum, da die Zellen in einer Lage auf der Oberfläche wachsen. In einem 3D-System haben die Zellen in allen 3 Ebenen Kontakte. Entweder nur zur Oberfläche oder zu Nachbarzellen rings herum.
|
3D systems are generated by culture in/on::
|
|
How do cells in 2D and 3D models differ?
2D and 3D culture models result in highly different cells and models. This means that neither the cells nor the results are same some times not even comparable. The following chracteristics and attributes of cells differ in the two model systems:
|
 |
 |
Advantages and disadvantages of 2D versus 3D cell culture?
In summary the following advantages and disadvantages of 2D/3D cell culture are known.
| 2D cell culture | 3D cell culture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3D-cell culture models
|
Cells can be cultured in 3D in many differents ways or, models or settings. Below we summarized some of the most important culture systems and examples for 3D models:
|
|
Special culture materials
|
In order to cultivate cells in 3D systems several special materials and substances are needed. This includes e.g.
|
|
Examples
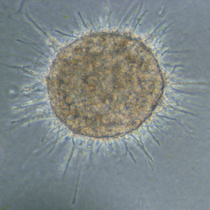
Generally spoken, sphäroids may be generated by 3 diffenrent mechanisms. Either they are plated on hydrophobic plastic surfaces that do not allow for adhesion, or cells are plated in hanging drops which do not offer any surface besides the membrane of the other cells because the cells sink into the hanging drop of medium, or öastly cells are cultured in special media that induce spheroid formation even on normal cell culture plastic surfaces that would allow for adhesion. One example, special hydrophobic plastic from PHCbi is shown below.