Cell banking - cryo-preservation of cells for pharmaceutical production and bioassays
|
The use of cell cultures (cell lines as well as primary cells) in pharmaceutical production as well as quality controle has drastically increased over the last years. In all fields of application, the frozen cell stocks are the basis for reliability and reproducibility of processes. In production, cells are either
In quality control labs, cells are
|
 |
Cell banking and control of pharmaceutical production cell banks (substrates)
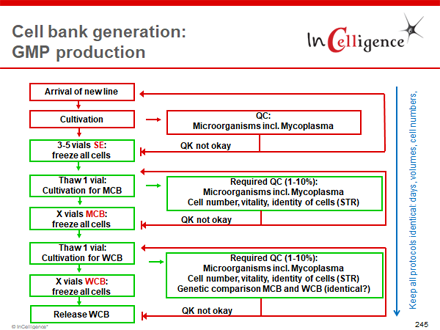
For cells used in vaccine production, the ICH Q5D Guideline "Derivation and Characterisation of Cell Substrates Used for Production of Biotechnological/Biological Products" (adopted EMA Guideline CPMP/ICH/294/95) regulates the basic requirements for the cells as well as the cell banking of Master (MCB) and Working Cell Bank (WCB), whereby the banking process is performed approximately as shown in the following diagram on the right.
|
§ 1 Introduction § 2 Guidelines § 2.1 Source, History, and Generation of the Cell Substrate § 2.1.1 Introduction § 2.1.2 Origin, Source, and History of Cells § 2.1.3 Generation of the Cell Substrate § 2.2. Cell Banking § 2.2.1 Cell Banking System § 2.2.2 Cell Banking Procedures § 2.3. General Principles of Characterization and Testing of Cell Banks § 2.3.1. Tests of Identity § 2.3.1.1 Metazoan Cells § 2.3.1.2 Microbial Cells § 2.3.2 Tests of Purity § 2.3.2.1 Metazoan Cells (viruses, bacteria, fungi, mycoplasma) § 2.3.2.2 Microbial Cells § 2.3.3 Cell Substrate Stability § 2.3.4 Tests for Karyology and Tumorigenicity |
|
Within the banking of production lines, all controls and tests performed must comply with the specifications and detection limits of the pharmacopoeia. This also applies to sterility tests, tests for viruses and mycoplasma.
Specifications for cell banks in the area of quality control and bioassays
In essence, cells used for QC testing are test devices and must be qualified and maintained as such. This means that their functionality must be tested initially and continuously. However, unlike manufacturing benches, contamination, for example, is not associated with any direct risk to the patient. Therefore, the scope and depth of testing can be reduced based on risk. Tests do not have to meet the specifications or detection limits of the pharmacopoiea. However, to date, there is no regulatory document that summarizes or explains the requirements for these cells.
The following points should also be implemented for bioassay cells in analogy to ICH Q5D:
- Documented origin
- Proof of identity (STR, DNA banding or karyogram) MCB, WCB
- Sterility testing (basal or EP compliant)
- Mycoplasma testing (basal or EP compliant)
- Banking
- Stability testing
In addition to the basic principles, one should always consider the aging problem when setting up a cell bank and strive for a banking system that guarantees a consistent quality of cells over a long period of time, if possible without the need to purchase new lines. Often it can be useful to generate further banking levels like safety freezes, primary or seeding cell banks to secure the demand in the long term.